The World Wide Web ("WWW" or "The Web") is a tool which began in the 60s, used by billions of people to share, read, and write information. Also, it was used to interact with other people via the internet, and was only a basic browser. After some years, HTML appears making the pages more friendly and easy to access.
In this article, you will find more information about the evolution from web 1.0 to web 2.0 to web 3.0 over the years.
Web 1.0
The goal of web 1.0 was to provide a shared information space for internet users and to facilitate communication through sharing information. It was, however, unorganized and overpowering.
Web 1.0 was regarded as a read-only web with little interaction, in which users may share information but not interact with the website.
The basic web protocols HTML, HTTP, and URL are included in Web 1.0 technologies. The following are the main characteristics of Web 1.0:
- They've only read the content.
- Create a web presence and make their information accessible at all times to anyone.
- It consists of static web pages.
- The content on the web pages is only understandable by humans (web readers), and it is not machine compatible.
- Email, fax, phone number, and address are included in the contact information.
Web 2.0
Web 2.0 refers to the second generation of the internet. Then, in the mid-2000s, came Web 2.0. Google, Amazon, Flickr, Facebook, and Twitter were created to provide order to the Internet by making it simple to connect and transact online. Critics claim that these corporations have accumulated far too much influence over time.
Rich web applications, web-oriented architecture, and social web are all part of the Web 2.0 concept. It refers to changes in the design and use of web sites by users. Text and hyperlinks are no longer the only components of a website. So, the pages are much more friendly and easy to access.
The main characteristic of Web 2.0 are:
- Centralizing customer information in a single secure database
- Storage of information on secure servers against theft, fire, power outage, etc.
- Compatibility with any device with a browser like PC, SmartPhones, PDAs, game consoles, etc.
- Ability to work multiple parallel users sharing the same data in real time
Information overload is a problem for Web 2.0. Users become confused and the content loses its reliability as a result of the enormous amount of information provided every day by many creators with various mindsets. Fake IDs, spammers, forgeries, and hackers who perform malicious activities are abundant on the present version of the internet due to the information being centralized .
Web 3.0
Web 3.0 is a sometimes used term for a mix of various ideas aimed at removing the internet's huge middlemen. Navigating the web in this new era no longer involves signing up for Facebook, Google, or Twitter.
The issue with Web 2.0 wasn't so much the content as it was the framework. Web 2.0's centralized nature provides the door to security issues, data collection for malicious purposes, privacy invasion, and expense. Web 3.0's major goal is to make it easier for web users to submit data in a way that computers can interpret, process, and share. This would allow web applications to execute time-consuming operations such as collating data from numerous sources and rapidly searching for relevant information based on user needs. Blockchain is becoming the core of Web 3.0 thanks to its decentralized, peer-to-peer, and secure network.
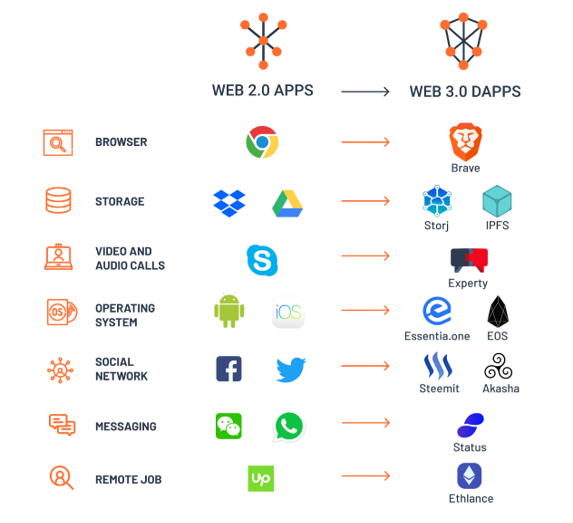
Crypto-based phones, VPNs, decentralized storage, and cryptocurrency wallets will all be popular in the not-too-distant future. Web 3.0, on the other hand, is about several profit centers exchanging value across an open network. The transition from Web 2.0 to Web 3.0 powered by Blockchain will be slow, as with any developing technology. Though the transformation is gradual and visually Web 2.0-friendly, the infrastructure that connects people to digital services is significantly different. As illustrated below, Web 2.0 Apps will be eventually superseded by Web 3.0 Dapps (Decentralized applications):
Web 3.0 is a sometimes used term for a mix of various ideas aimed at removing the internet's huge middlemen. Navigating the web in this new era no longer involves signing up for Facebook, Google, or Twitter.
The issue with Web 2.0 wasn't so much the content as it was the framework. Web 2.0's centralized nature provides the door to security issues, data collection for malicious purposes, privacy invasion, and expense. Web 3.0's major goal is to make it easier for web users to submit data in a way that computers can interpret, process, and share. This would allow web applications to execute time-consuming operations such as collating data from numerous sources and rapidly searching for relevant information based on user needs. Blockchain is becoming the core of Web 3.0 thanks to its decentralized, peer-to-peer, and secure network.
Crypto-based phones, VPNs, decentralized storage, and cryptocurrency wallets will all be popular in the not-too-distant future. Web 3.0, on the other hand, is about several profit centers exchanging value across an open network. The transition from Web 2.0 to Web 3.0 powered by Blockchain will be slow, as with any developing technology. Though the transformation is gradual and visually Web 2.0-friendly, the infrastructure that connects people to digital services is significantly different. As illustrated below, Web 2.0 Apps will be eventually superseded by Web 3.0 Dapps (Decentralized applications):
Web 3.0 is a sometimes used term for a mix of various ideas aimed at removing the internet's huge middlemen. Navigating the web in this new era no longer involves signing up for Facebook, Google, or Twitter.
The issue with Web 2.0 wasn't so much the content as it was the framework. Web 2.0's centralized nature provides the door to security issues, data collection for malicious purposes, privacy invasion, and expense. Web 3.0's major goal is to make it easier for web users to submit data in a way that computers can interpret, process, and share. This would allow web applications to execute time-consuming operations such as collating data from numerous sources and rapidly searching for relevant information based on user needs. Blockchain is becoming the core of Web 3.0 thanks to its decentralized, peer-to-peer, and secure network.
Crypto-based phones, VPNs, decentralized storage, and cryptocurrency wallets will all be popular in the not-too-distant future. Web 3.0, on the other hand, is about several profit centers exchanging value across an open network. The transition from Web 2.0 to Web 3.0 powered by Blockchain will be slow, as with any developing technology. Though the transformation is gradual and visually Web 2.0-friendly, the infrastructure that connects people to digital services is significantly different. As illustrated below, Web 2.0 Apps will be eventually superseded by Web 3.0 Dapps (Decentralized applications):
Advantages of Web 3.0
Decentralized Web: Web 3.0, which is supported by blockchain, will ensure that organizations like Alphabet and Apple lose ownership of user data. Intermediaries would be removed from the equation in Web 3.0, and Blockchain platforms would provide a trustless platform with unbreakable rules and fully encrypted data. There would also be no central point of control because no government or corporation would be able to shut down sites or services, and no single person would be able to control the identities of others.
Ownership of Data: Information could be shared on a case-by-case and permissioned basis using Web 3.0. Global giants like Amazon and Facebook now have factories of servers keeping data on dietary choices, income, interests, credit card numbers, and other personal information. End-users will recover entire ownership of data on Web 3.0, as these corporations sell this data to advertising for billions.
Reduction in Hacks and Data Breaches: Data would be decentralized and distributed across the network on a Blockchain-enabled Web Platform. Hackers would have to work on the entire chain of blocks and switch off the entire network to change or hack any user information, which is nearly impossible. Every day, we hear about cyber-attacks that not only jeopardize the security of people but also constitute a national security concern. This occurs as a result of internet corporations being forced to fork up customer data or risk having their entire database inspected. Data is more valuable than gold in the digital age, and data breaches cost the global economy trillions of dollars every year.
The movement from Web 2.0 to Web 3.0 is causing a revolution. A new and interesting Social Semantic Web environment would emerge if Web 2.0 application design principles were combined with Web 3.0 logics and knowledge management.
Status Contribution into the Web 3.0 revolution
Status is an open source decentralized messaging platform, non-custodial crypto wallet, and web 3.0 browser meant to operate as a network node that interacts with Ethereum-based decentralized applications (DApps).
Nimbus
Nimbus is a client implementation for both Ethereum's consensus layer (eth2) and execution layer (eth1) that aims to be as resource-light as possible. This enables it to perform well on embedded systems and embedded devices such as Raspberry Pis and mobile devices.
However, Nimbus is useful for more than just resource-constrained hardware. Because of its low resource consumption, Nimbus can coexist with other workloads on your server (this is especially valuable for stakers looking to lower the cost of their server instances).
Nim is a general-purpose systems programming language that compiles to C and has a Python-like syntax. Nim enables us to quickly implement Ethereum while taking advantage of mature C-language tooling: compilation of machine code and static code analysis.
The end result of Nim implementation is code that:
- Allows us to easily transition research into production.
- For researchers, it has a high level of reasonability.
- Is it efficient in production?
The Nim core contributors and the larger Nim community have been extremely supportive of this decision.
Nimbus is an open source project in which anyone can participate. There are several ways to contribute and if you are interested to join us, please click here.
Waku
Third-party interference is common in today's communication. From censorship and deplatforming to rent-seeking intermediaries and data misuse in the surveillance economy. Waku is intended to re-establish individual control over communication.
Waku is Web3's communication layer. Scalable decentralized communication It is private, secure, and can be used anywhere. It is based on the Whisper protocol, but it has been optimized for scalability and usability.
Waku eliminates the need for centralized third parties in our messaging, allowing for private, secure, and censorship-free communication. Also, it is intended for generalized messaging, allowing for both human-to-human and machine-to-machine communication. Digital signature, public key difficulty hashrate whitepaper, Merkle Tree double-spend Mempool outputs, double-spend problem?
Privacy: These applications desire privacy guarantees such as pseudonymity, metadata protection in transit, and so on.
Generalized messaging: Many applications require some kind of messaging protocol to communicate between different subsystems or nodes. This messaging can be human-to-human, machine-to-machine, or a combination of both.
Peer-to-Peer: These applications may have requirements that make them suitable for peer-to-peer solutions.
Resources are scarce: These applications are frequently run in constrained environments, where resources or the environment are restricted in some way. E.g.: limited bandwidth, CPU, memory, disk, battery, etc., not publicly connectable, only intermittently connected; mostly offline.
Resume
Status is a secure messaging app, crypto wallet, and Web3 browser built with state of the art technology. So, the Status Network is a decentralized application ecosystem that aims to create private, secure communication solutions. We advocate for the protection of human rights and the empowerment of sovereign communities, allowing anybody with a smartphone and internet access to access indisputable free commerce, peer-to-peer payments, and encrypted peer-to-peer communication.Do not hesitate to download the Status App right now to become part of this huge Web 3.0 movement. You can get it here.